What is Sugarcane?
Sugarcane is a tall perennial grass that is cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. Is a species of grass that belongs to the genus Saccharum, and family Poaceae.
- It grows between 2-6 meters (6-20 feet) tall with thick, jointed fibrous stalks.
- The sugar content is concentrated in the stem internodes, not the leaves or roots.
- It is a C4 plant, which means it has high photosynthetic efficiency and productivity in hot environments.
- The main sugar present is sucrose, which accumulates in the stalk internodes as the plant matures.
- After harvesting, the canes are crushed in mills to extract the juice, which is then processed to crystallize the sucrose into raw sugar.
- Sugarcane accounts for about 80% of the world's sugar production, with the remaining from sugar beets.
- Leading sugarcane producers include Brazil, India, China, Thailand, and Mexico.
- In addition to sugar, byproducts include molasses and ethanol from fermentation of the juice.

Sugar Directorate Report
According to Sugar Directorate in February 2024 Sugar Market News report:
- Total sugarcane milled by all sugar factories increased to 755,996 MT in February 2024, up from 713,513 MT in January 2024.
- Sugar made also increased to 63,541 MT from 61,131 MT in January 2024.
- The industry average cane to sugar ratio (TC/TS) in February 2024 was 11.9, which indicates the efficiency of sugarcane conversion to sugar.
UN SDG 13: Climate Action
Sugarcane cultivation and production contributes to climate action (SDG 13) in several ways:
- Sugarcane bagasse (the fibrous residue after juice extraction) can be used as a renewable biofuel for generating electricity or heat, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
- Ethanol produced from sugarcane fermentation can be used as a biofuel for transportation, offering a more sustainable alternative to gasoline and diesel.
- Sustainable sugarcane farming practices, such as efficient water management, reduced use of synthetic fertilizers, and conservation of soil quality, can help mitigate environmental impacts and improve climate resilience.
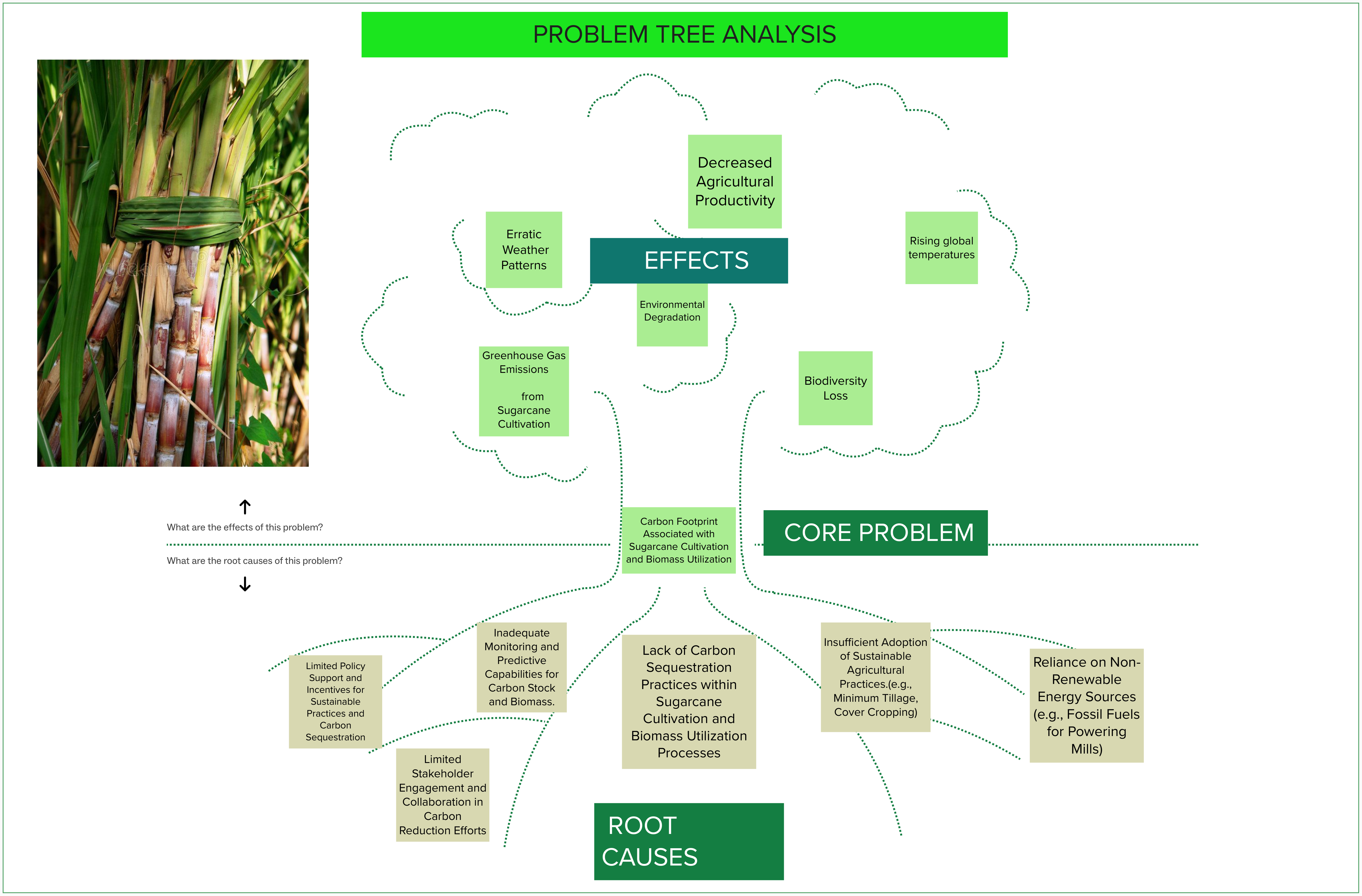
Carbon Footprint and Sugarcane
While sugarcane production can contribute to climate action through biofuel and sustainable practices, it is important to consider its carbon footprint:
- Sugarcane cultivation requires significant land use, which can lead to deforestation and loss of carbon sinks if not managed sustainably.
- The burning of sugarcane fields before harvesting, a common practice in some regions, releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- The transportation and processing of sugarcane also contribute to carbon emissions through the use of fossil fuels for machinery and energy.

To minimize the carbon footprint and maximize the sustainability of sugarcane production, it is crucial to adopt sustainable farming practices, invest in renewable energy sources for processing, and promote efficient transportation and distribution systems.